Click here and press the right key for the next slide.
(This may not work on mobile or ipad. You can try using chrome or firefox, but even that may fail. Sorry.)
also ...
Press the left key to go backwards (or swipe right)
Press n to toggle whether notes are shown (or add '?notes' to the url before the #)
Press m or double tap to slide thumbnails (menu)
Press ? at any time to show the keyboard shortcuts
A Dual Process Theory of Mindreading

A Dual Process Theory of Mindreading
[email protected]
A-tasks
Children fail
because they rely on a model of minds and actions that does not incorporate beliefs
non-A-tasks
Children pass
by relying on a model of minds and actions that does incorporate beliefs
dogma
the
of mindreading
Q1
How do observations about tracking support conclusions about representing models?
Q2
Why are there dissociations in nonhuman apes’, human infants’ and human adults’ performance on belief-tracking tasks?
1. models [done]
2. processes
- reasoning and inference (Evans, 2003)
- judgement and decision-making (Kahneman, 2002)
- memory (Jacoby, 1991)
- social cognition (Gawronski, Sherman, & Trope, 2014)
- mindreading (Apperly & Butterfill, 2009)
- number (Feigenson, Dehaene, & Spelke, 2004)
- ethics (Greene, Nystrom, Engell, Darley, & Cohen, 2004)
- instrumental behaviour (Dickinson & Pérez, 2018)
- learning (Dayan & Berridge, 2014)
- ? social norms (Bicchieri, 2016)
- ? physical cognition (Kozhevnikov & Hegarty, 2001)
- ? categorical colour (Gilbert, Regier, & Ivry, 2006)
- ? vision (Goodale & Milner, 1992)
- ? agency (Sidarus, Vuorre, & Haggard, 2017)
implicit / modular
/ ‘system-1’ / ...
innate
informationally encapsulated
domain specific
subject to limited accessibility
speedy
tacit
subpersonal
unconscious
...
‘it seems doubtful that the often long lists of correlated attributes should come as a package’
Adolphs (2010 p. 759)
‘we wonder whether the dichotomous characteristics … are … perfectly correlated
Keren and Schul (2009, p. 537)
a fresh start
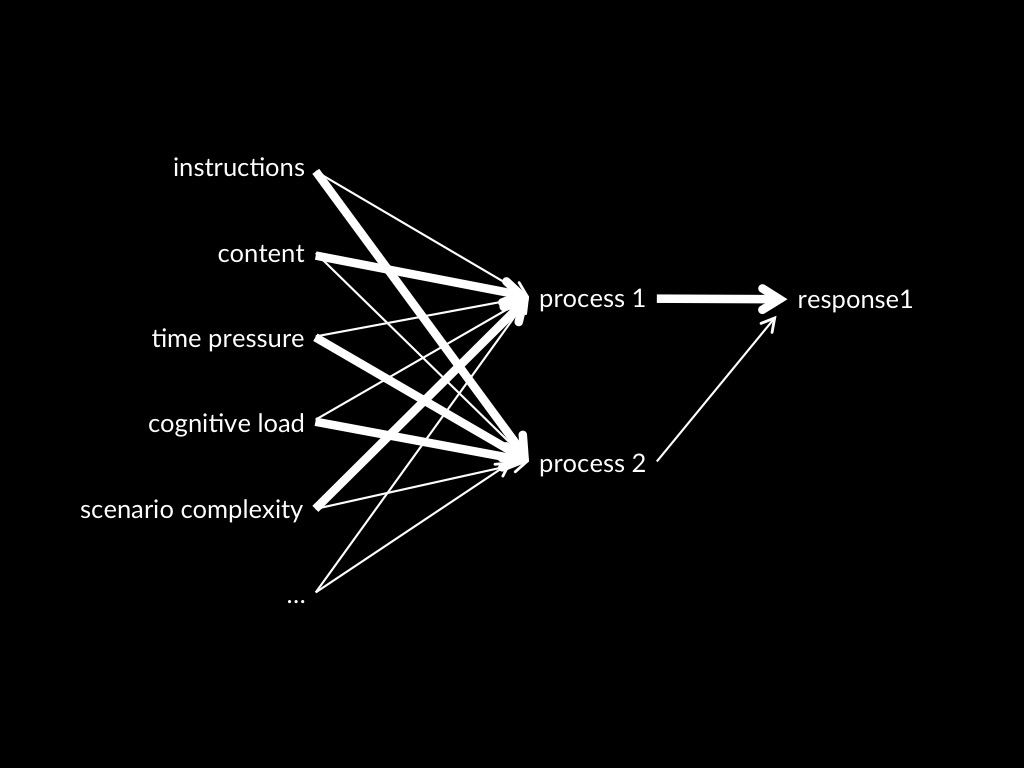
Process 1 -> Response 1
Process 2 -> Response 2

Dual Process Theory of Mindreading (core part)
Two (or more) mindreading processes are distinct:
the conditions which influence whether they occur,
and which outputs they generate,
do not completely overlap.
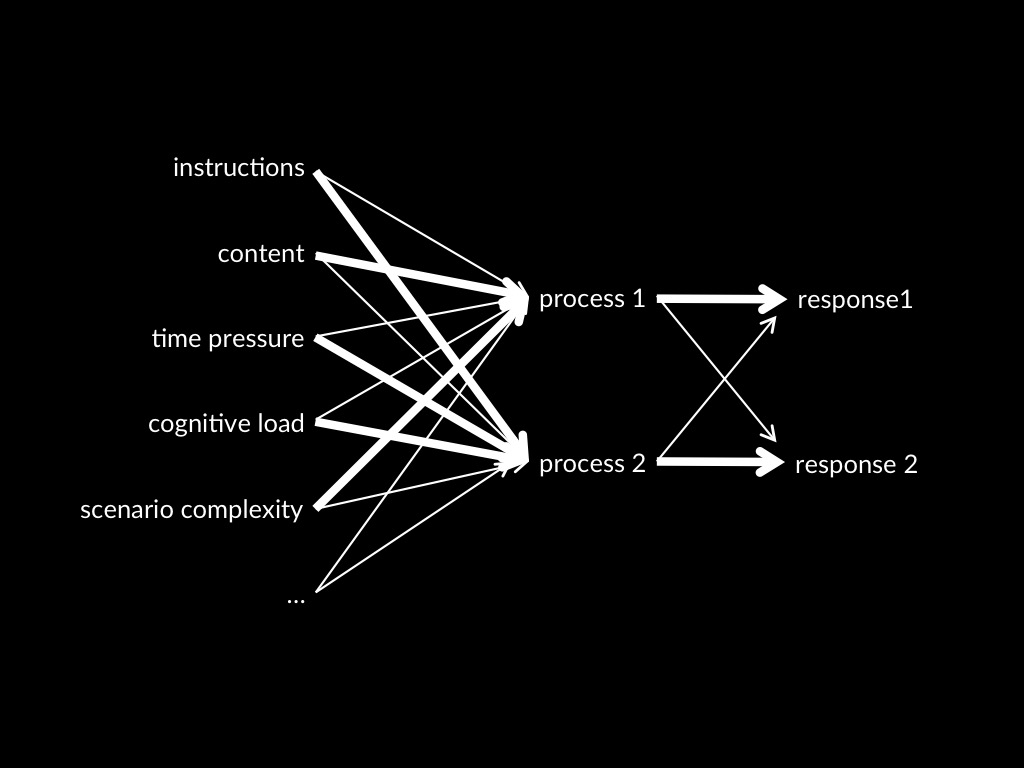
Process 1 -> Response 1
Process 2 -> Response 2
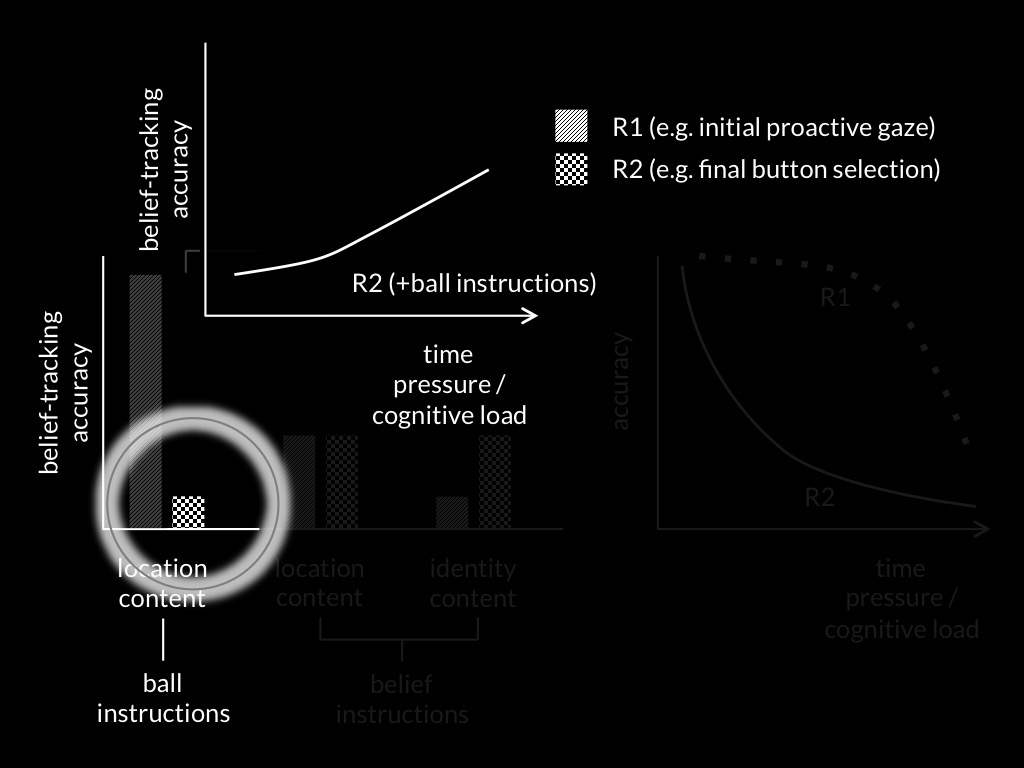

Dual Process Theory of Mindreading (core part)
Two (or more) mindreading processes are distinct:
the conditions which influence whether they occur,
and which outputs they generate,
do not completely overlap.
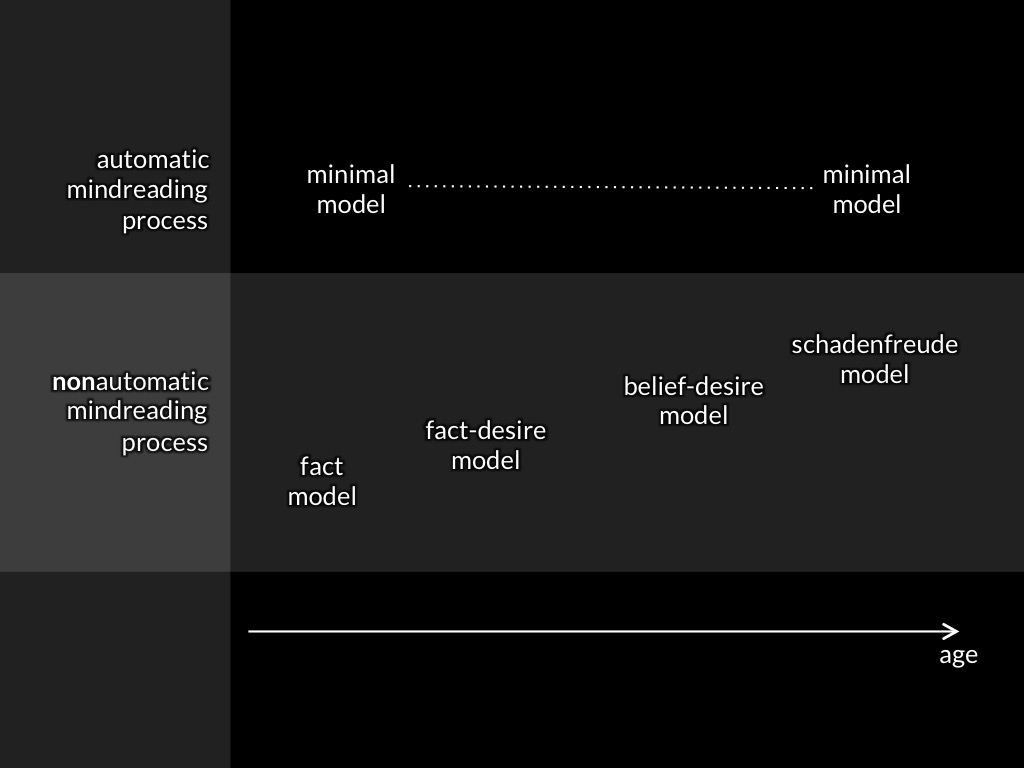
What about development?

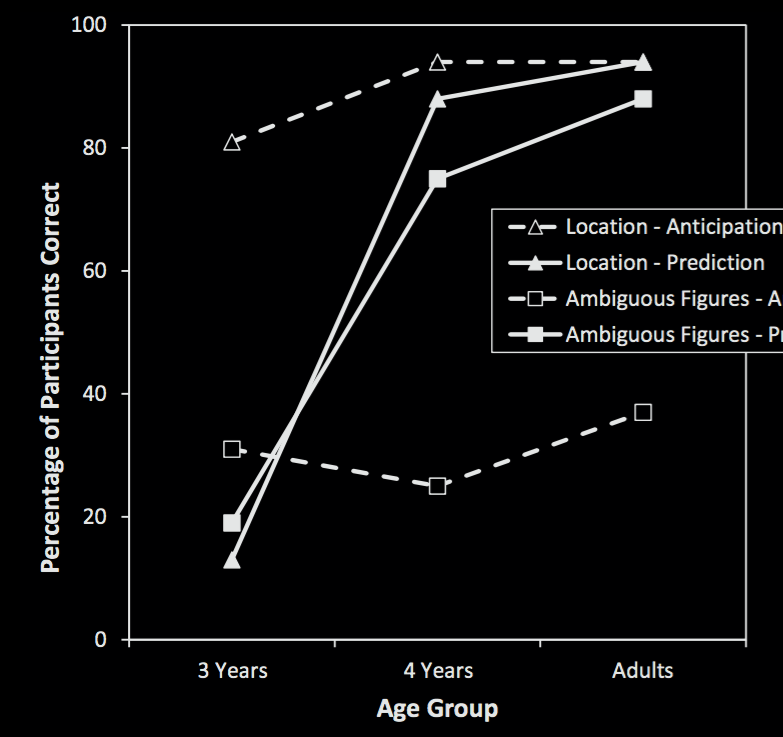
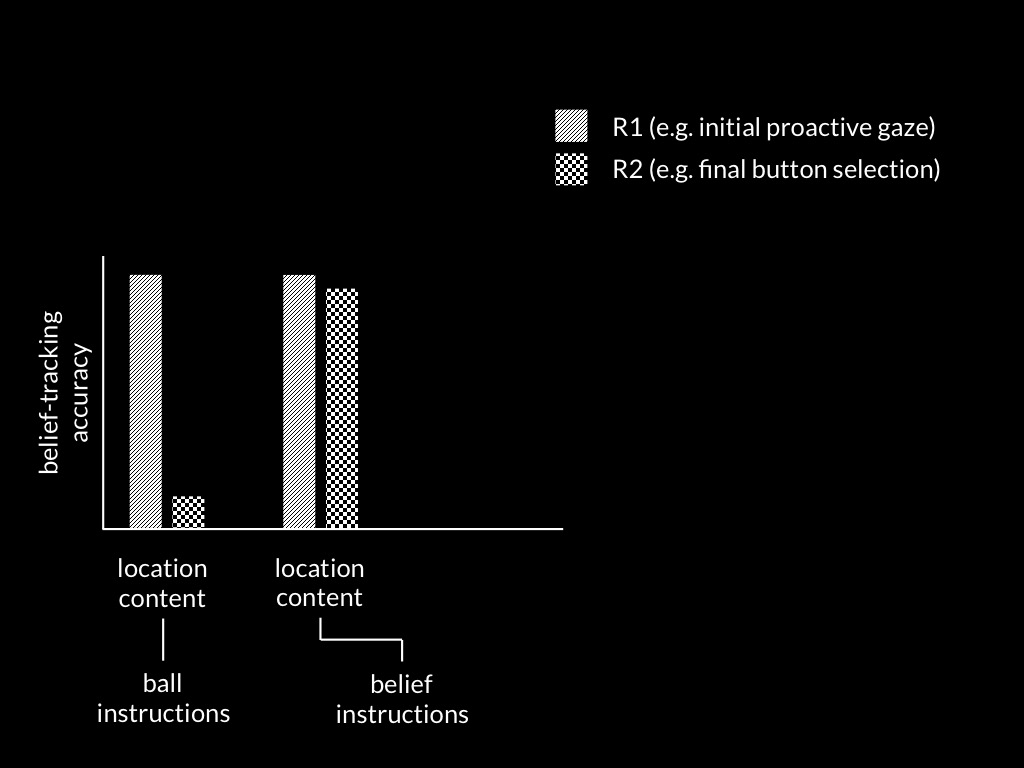
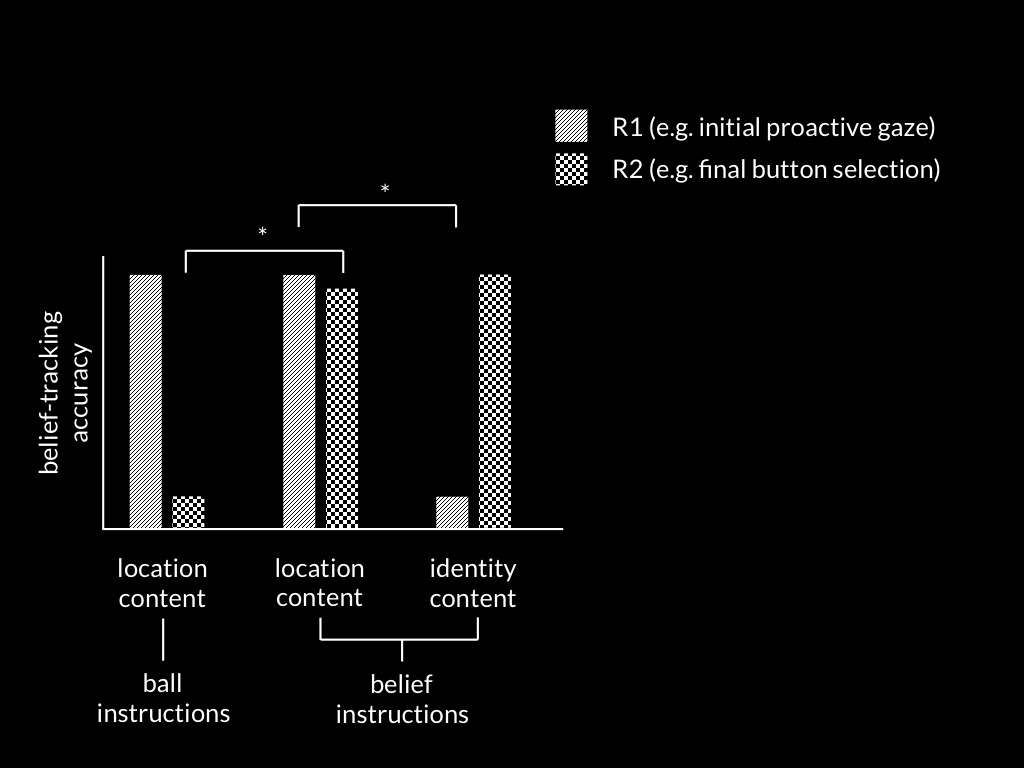
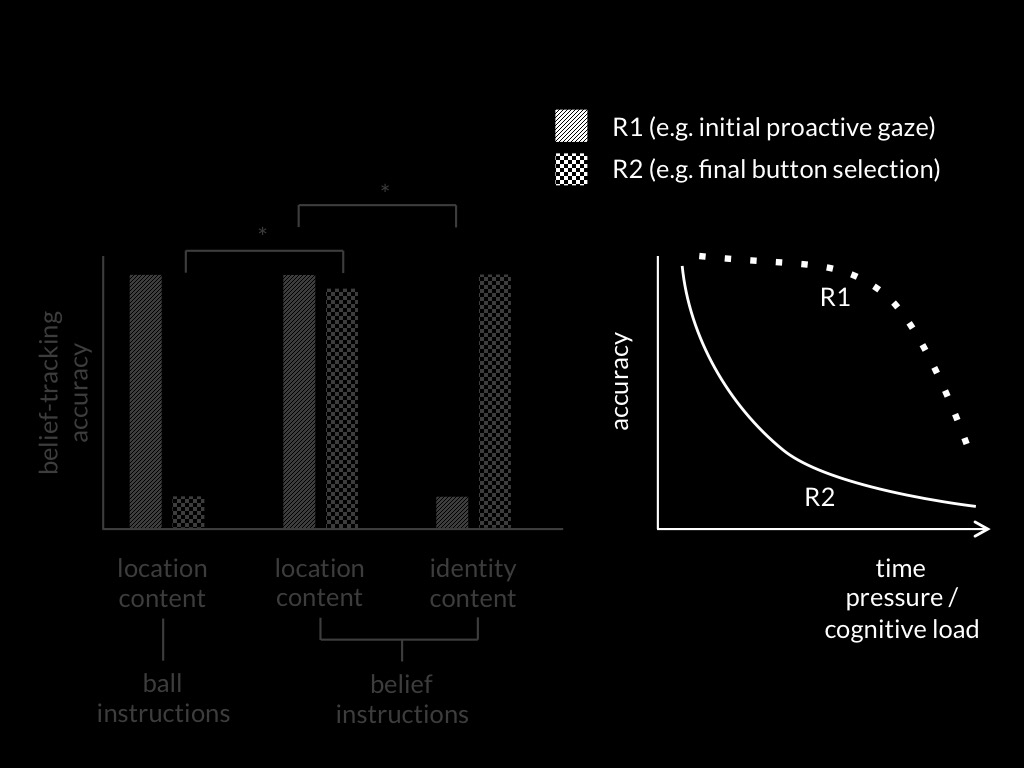
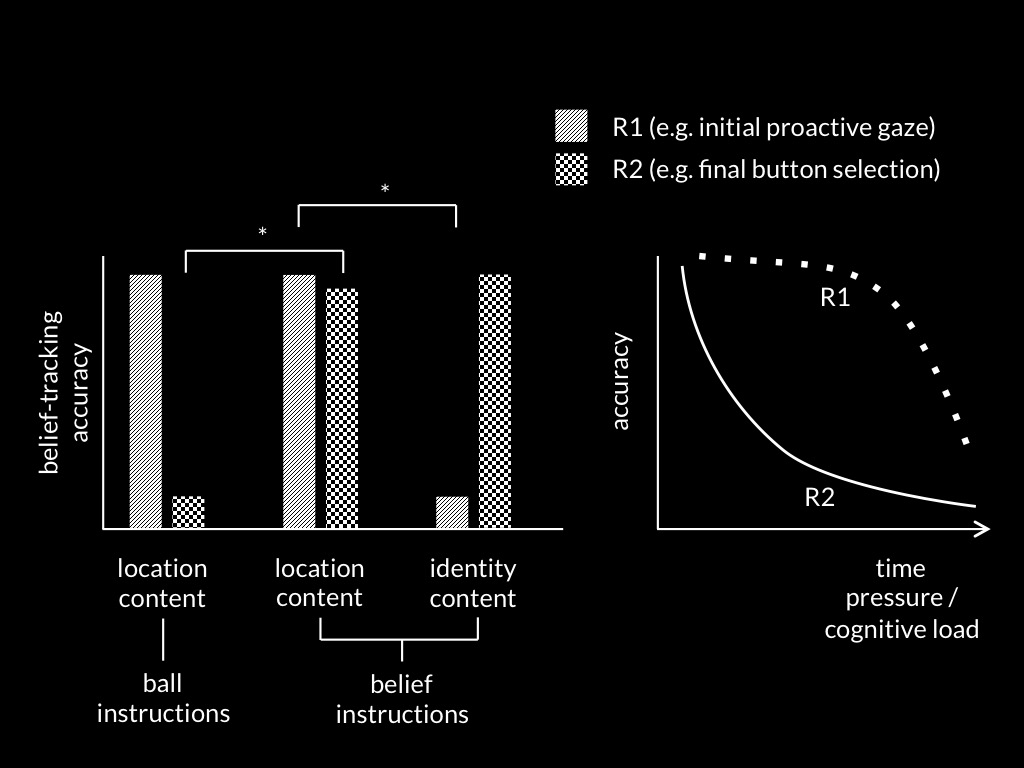
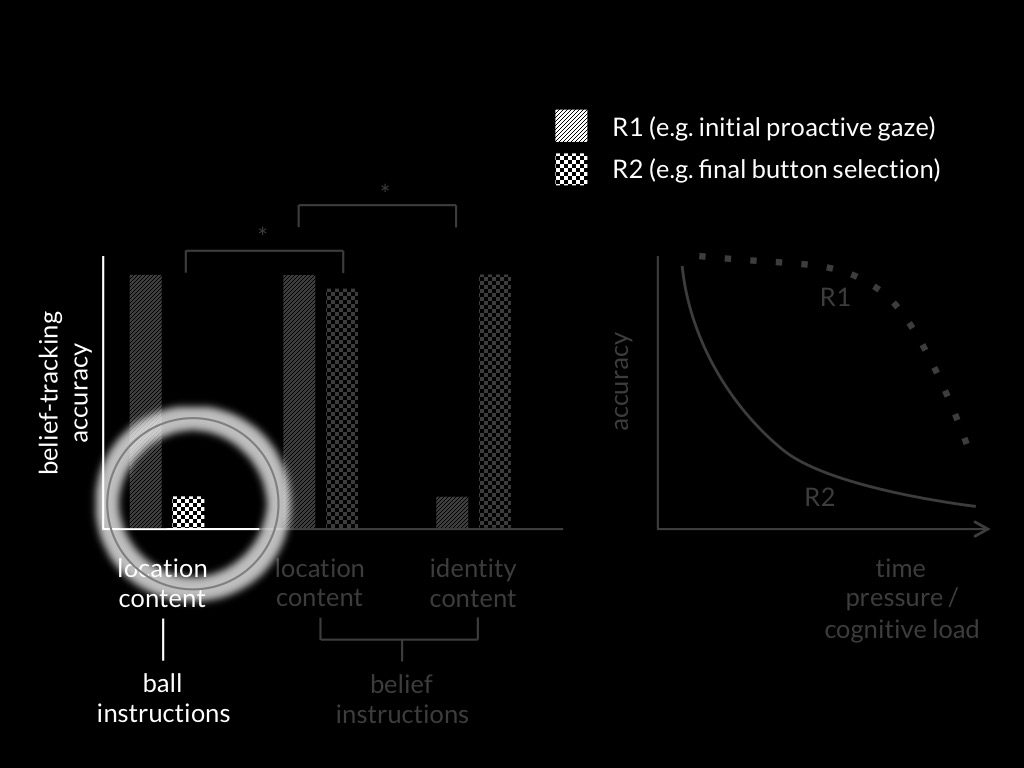
Low et al, 2014 figure 2
Q1
How do observations about tracking support conclusions about representing models?
Q2
Why are there dissociations in nonhuman apes’, human infants’ and human adults’ performance on belief-tracking tasks?
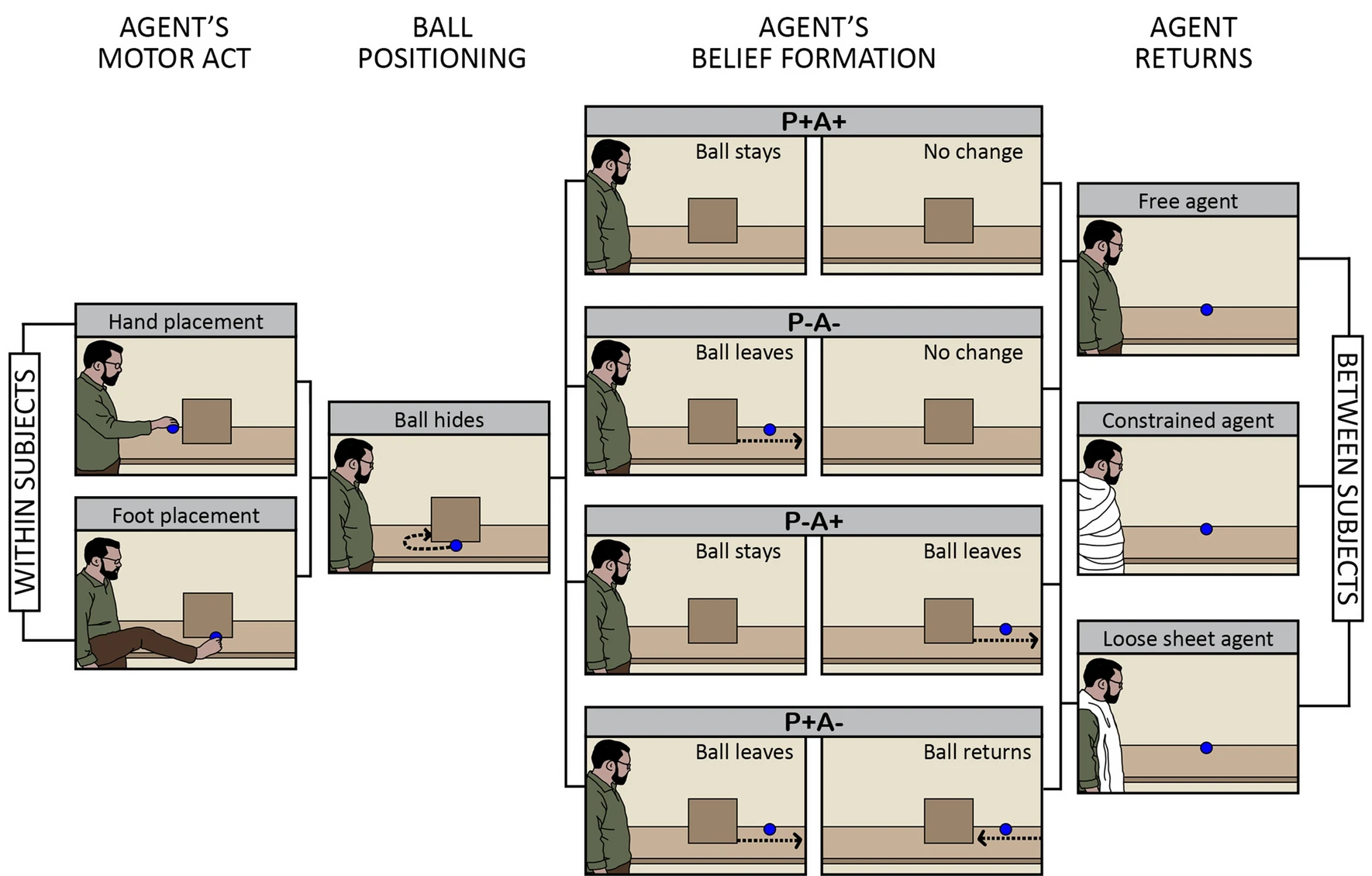
(Low, Edwards, & Butterfill, 2020, p. figure 1)
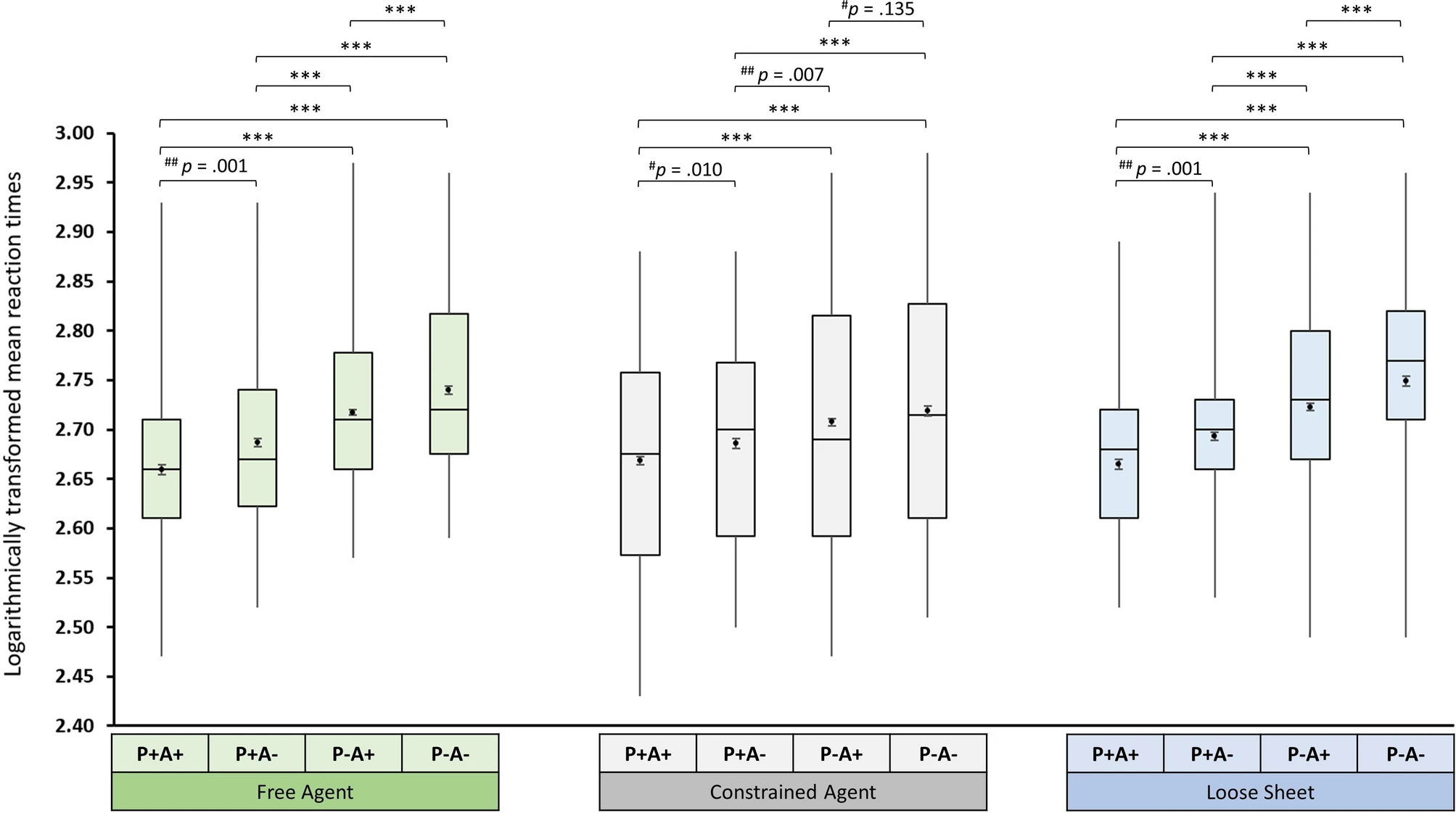
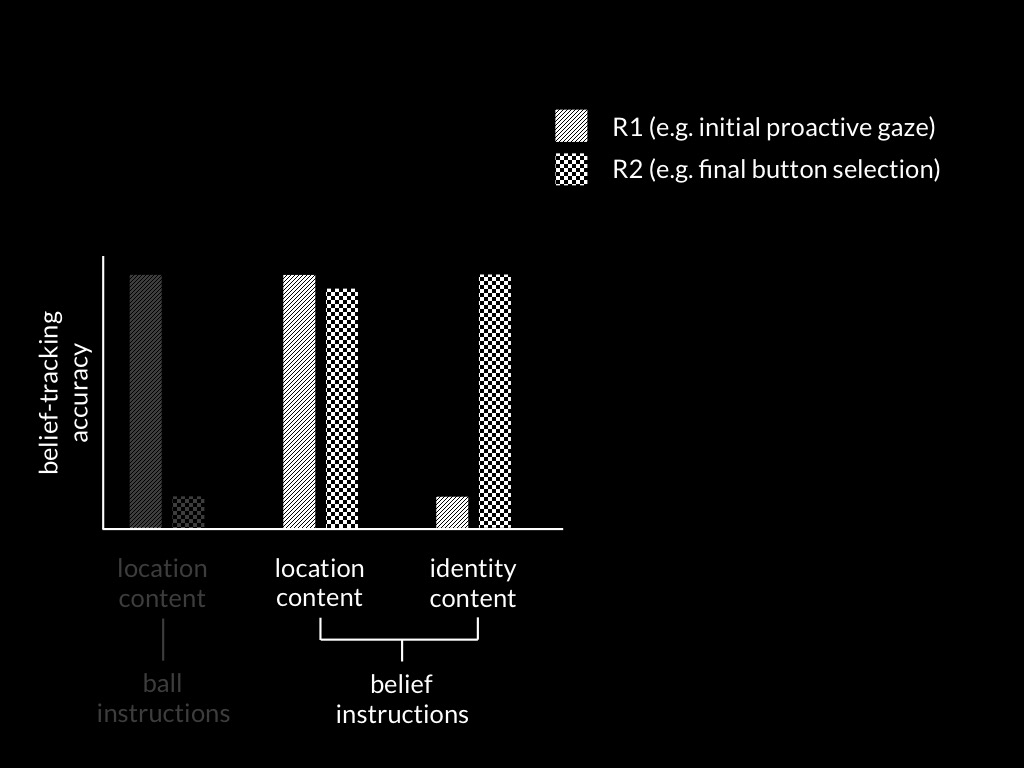
(Low et al., 2020, p. figure 2)
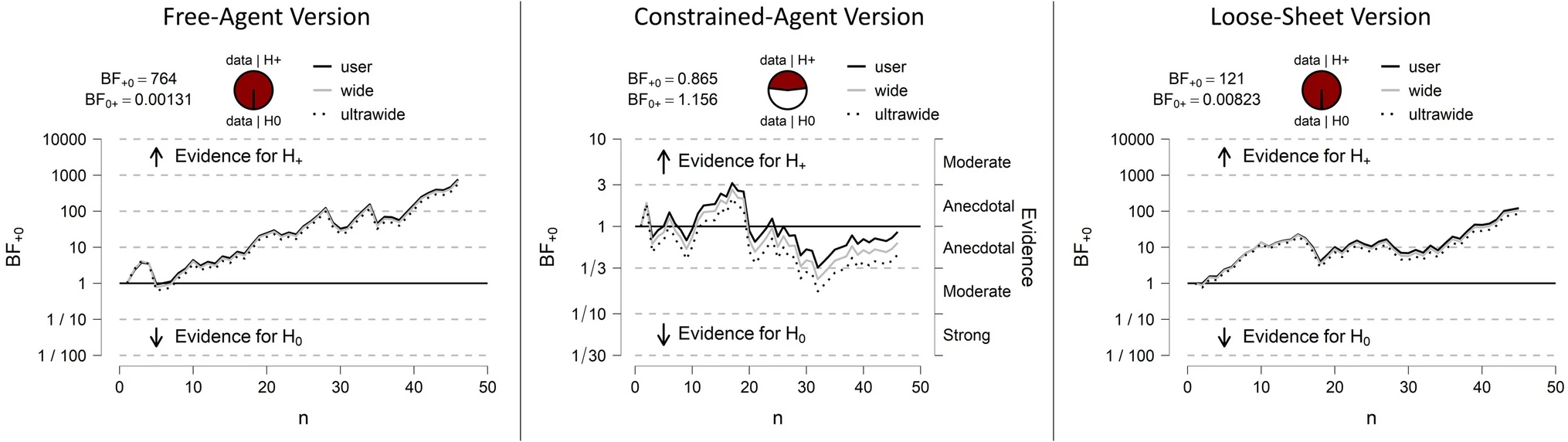
(Low et al., 2020, p. figure 3)
A-tasks
Children fail
because they rely on a model of minds and actions that does not incorporate beliefs
non-A-tasks
Children pass
by relying on a model of minds and actions that does incorporate beliefs
dogma
the
of mindreading